Introduction
Tetanus is a dangerous infectious disease characterized by muscle spasms. It is caused by the toxins (potent neurotoxin) secreted by a bacterium known as Clostridium tetani. Tetanus may occur at any age, and case-fatality rates are high even with intensive care. Without medical care, the case-fatality rate is almost 100%.
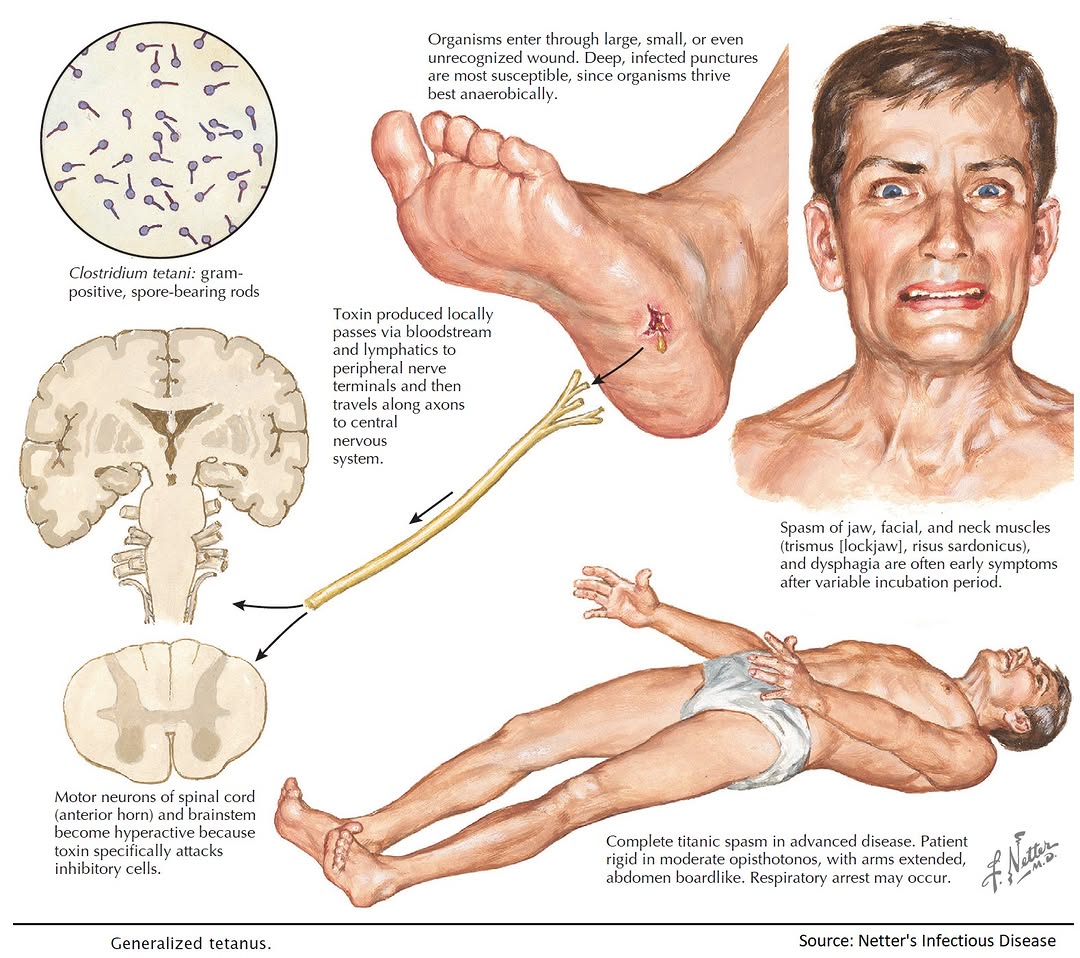
Mechanism:
The bacteria survive as spores in soil. These spores are ubiquitous around the world and may remain infectious for a very long time, more than 40 years. Once the spores gain entry into the body through a breach in the skin caused by any injury (or through the umbilical cord stump in the neonate), they germinate under anaerobic conditions.
These bacteria secrete a very potent toxin (tetanospasmin) that enters the blood and reaches the central nervous system (CNS). The toxin bound to CNS causes the typical signs and symptoms of tetanus, which has a high mortality.
What are the aims of tetanus prophylaxis following injury?
- Timely removal of C. tetani from the wound/s before they can produce critical amounts of toxin
- Deactivate any toxin that has already been absorbed from the wound/s before it can reach the CNS.
Algorithm for tetanus vaccination after injury:
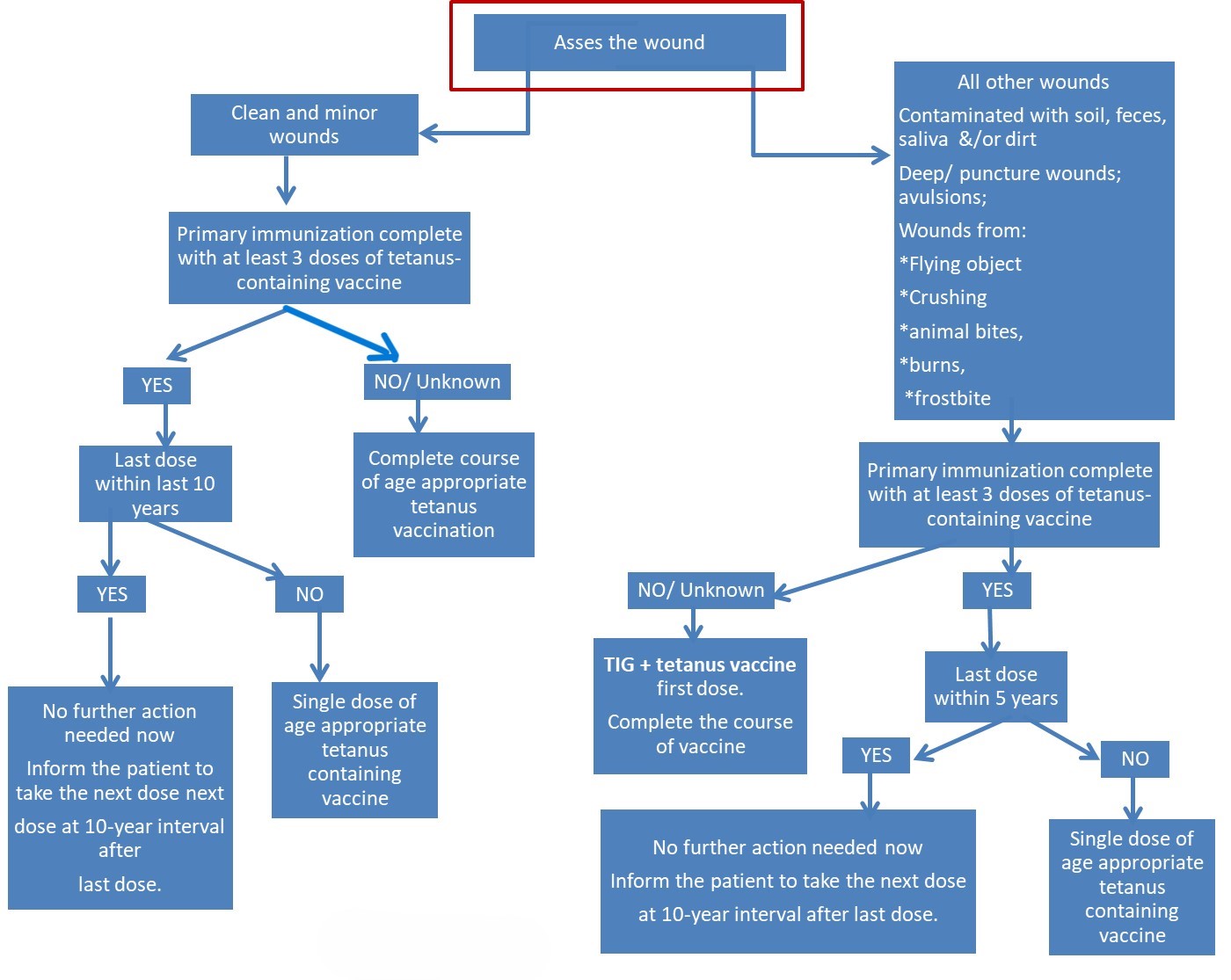
The most commonly used tetanus vaccine following injury, after 5 years of age, has been Tetanus Toxoid (TT) till recently. The Government of India, since 2018, has started replacing the TT vaccine with the Td vaccine in a phased manner for all age groups, including pregnant women. This step is in consideration of increasing numbers of cases of diphtheria in older age groups in India and other countries.
In pregnancy:
- First dose at the confirmation of pregnancy
- Second dose after four weeks of the first dose of the tetanus toxoid vaccine.
In infants:
- No vaccine or TIG is recommended for infants younger than 6 weeks of age with clean, minor wounds. (And no vaccine is licensed for infants younger than 6 weeks of age.)
- For infants younger than 6 weeks of age, TIG (without vaccine) is recommended for ”dirty” wounds (wounds other than clean, minor ones).
In immunocompromised:
Persons who are HIV positive should receive TIG regardless of tetanus immunization history.
How to give a tetanus vaccine?
- Dose: 0.5 ml intramuscularly
- Preferred site: Deltoid
Tetanus Immunoglobulin (TIG):
When to give:
- Dirty wound + No/unknown primary immunization
- Infants < 6 weeks of age
How to give: 500 IU intramuscularly, single dose
If TIG isn't available, healthcare providers can use immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) (dose 200 to 400 milligrams per kilogram).
Age-appropriate vaccine:
- DTaP (Tetanus, Diphtheria, and acellular Pertussis) for 6 weeks up to 7 years of age (or DT pediatric if the pertussis vaccine is contraindicated)
- Td (combination of tetanus and diphtheria with lower concentration of diphtheria antigen) for persons 7-9 years of age and >65 years of age
- Tdap for >10 years of age unless the person has received a prior dose of Tdap
References:
https://ihatepsm.com/blog/tetanus-prophylaxis-after-injury
https://www.health.state.mn.us/diseases/tetanus/hcp/tetwdmgmtc.pdf