Introduction:
Urinary incontinence, also known as involuntary urination, is the accidental loss of urine. It can range from occasional leakage to frequent wetting. Urinary incontinence can occur at any age, but it's more common in older people, especially women. There are several causes of urinary incontinence:
In women:
- Pregnancy & Childbirth
- Menopause
- Obesity
- Pelvic prolapse
In men:
- Prostate enlargement or infection
Common:
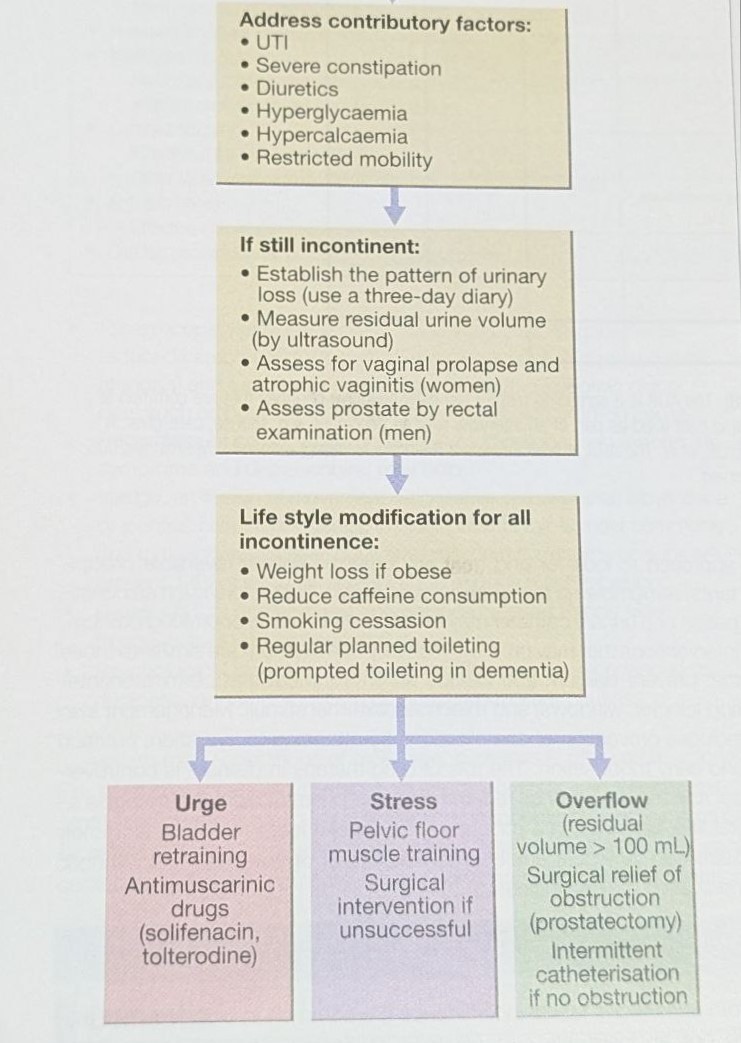
- Severe constipation
- UTI
- Diuretics
- Hyperglycemia, Hypercalcemia
- Nerve damage
- Restricted mobility
- Alcohol, Caffeine
- Cognitive impairment in old age
Types of incontinence:
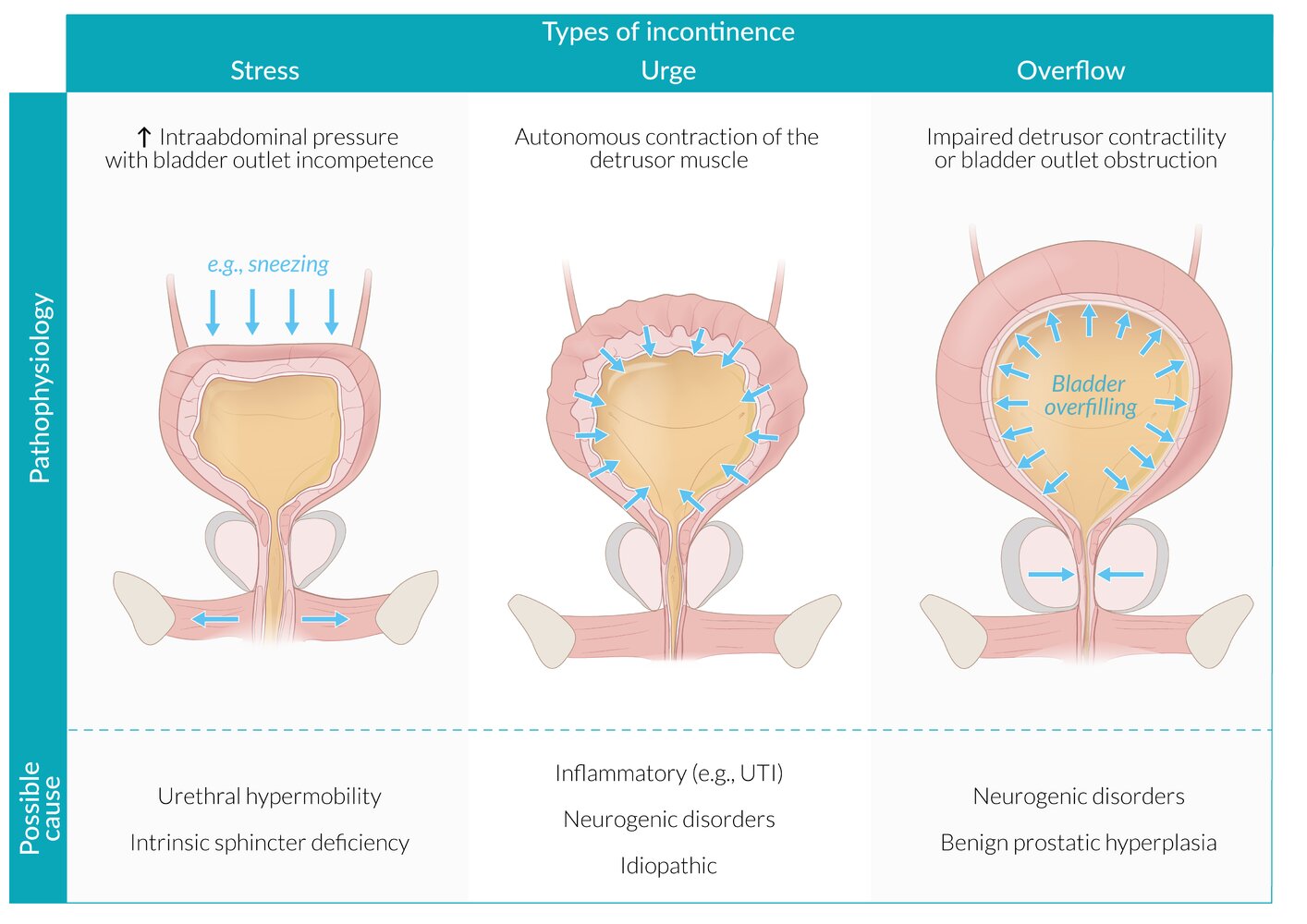
1. Urgency Incontinence: Involuntary urge to urinate that leads to uncontrollable voiding of urine.
Symptoms:
- Feeling the need to urinate frequently, including at night
- Needing to urinate suddenly and urgently
- Not being able to control when you pass urine
Reason: detrusor muscle overactivity
Main Causes:
- Infections
- neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or stroke
- Diabetes
- Bladder inflammation
- Bladder stones
2. Stress Incontinence: Leakage of urine when intraabdominal pressure rises.
Symptoms: Involuntary loss of urine during actions such as coughing, sneezing, and putting abdominal pressure.
Reason: Weakness of pelvic muscle floor
Main causes:
- Men—prostate surgery
- Women—pregnancy, childbirth, menopause
3. Overflow Incontinence: the bladder is unable to empty completely, resulting in the involuntary release of urine.
Symptoms: Constant dribbling of urine is usually associated with urinating frequently and in small amounts.
Reason: Obstruction of bladder outflow
Main Causes:
- Blockage in the urinary tract, such as from an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer
- Weak bladder muscles
- Nerve damage, such as from surgery or a spinal cord injury
Assessment and Management Algorithm:
Antimuscarinic Drugs in Urge Incontinence:
1. Solifenacin - oral 5 mg OD; if tolerated, the dose may be increased to 10 mg OD
Dose adjustment:
- Hepatic impairment: mild (use with caution), moderate (max 5 mg OD), severe (use not recommended)
- Renal impairment: CrCl >= 30 ml/min (use with caution); CrCl < 30 ml/min (max 5 mg OD)
Side Effects: Constipation, xerostomia, drowsiness, hypertension, urine retention, UTI, blurred vision
2. Tolterodine—immediate-release tablet (1-2 mg BID), extended-release tablet (2-4 mg OD)
Dose adjustment:
- Hepatic impairment: mild to moderate (use with caution), severe (use not recommended)
- Renal impairment: CrCl of 10-30 ml/min (use with caution); CrCl < 10 ml/min (not recommended)
Side Effects: similar to Solifenacin
Pelvic floor muscle Training in stress incontinence:
Pelvic floor muscle training exercises can help strengthen the muscles under the uterus, bladder, and bowel. One can try to feel their pelvic floor muscles by imagining stopping themselves from peeing or farting.
How to do:
- Empty your bladder.
- Tighten your pelvic floor muscles.
- Hold for a count of 10.
- Relax your muscles for a count of 10.
- Repeat 10 times, 3 to 5 times a day.
You might need to do PFMT for a few months before you notice any benefits.
What is intermittent catheterization (IC)?
Insertion and removal of a catheter several times a day to empty the bladder. It has a lower risk of UTI than an indwelling catheter, where the catheter is placed for a period of time.
References:
Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine, 24th Edition